Yes, a faulty motherboard can seriously damage your CPU, especially if there are power surges, overheating, or short circuits. Powerful protection, like proper cooling and using high-quality parts, can prevent costly damage. Always ensure your motherboard is in good condition to keep your CPU safe.
In this article, we will explore the scenarios where a motherboard could potentially harm a CPU, the safeguards to put in place, and how to ensure a safe and reliable system setup.
The Future of Motherboards and CPUs: Will 2026 Bring New Risks?
In 2026, motherboards and CPUs will likely see major advancements in speed, efficiency, and power. However, with new technology, there may be risks like security concerns and compatibility issues. Staying informed and upgrading carefully will be important to avoid these potential challenges and ensure smooth performance.
Can a mainboard damage a CPU?
Yes, a mainboard (motherboard) can damage a CPU if it is faulty or of low quality. This happens when the motherboard sends the wrong voltage, has power supply problems, or experiences a short circuit. A bad BIOS update can also harm your processor. Always use a trusted motherboard, a good power supply, and an updated BIOS to protect your CPU.
Can a CPU be bottlenecked by a motherboard?
Yes, a CPU can be bottlenecked by a motherboard if the board cannot handle the CPU’s full power. A low-end or old motherboard can limit CPU performance because of a weak power supply, slow RAM speed, or an outdated BIOS. Always choose a compatible motherboard so your CPU runs fast and smoothly without bottlenecks.
Can a Motherboard Bottleneck Your CPU Performance?
Yes, a motherboard can bottleneck your CPU’s performance if it lacks the necessary resources or support for high-end components. This typically happens if the motherboard has an older chipset, insufficient RAM slots, or lacks PCIe lanes required for modern GPUs. Even if you have a powerful CPU, a low-end motherboard can limit the CPU’s capabilities by not providing enough bandwidth for the processor to communicate efficiently with other components.
Many users buy powerful CPUs and GPUs, only to realize that their motherboard is limiting their potential. They may experience lower frame rates, slower data transfer speeds, and increased load times, leading to disappointment.
What Are the Signs of a Bad Motherboard?
A bad motherboard can manifest in several ways. Common signs include:
- No POST (Power-On Self-Test): If your system doesn’t boot, it might indicate a dead motherboard.
- Random Crashes: Frequent and unexplained crashes can point to issues with the motherboard’s power delivery or connections.
- Overheating: A failing motherboard may cause overheating due to poor voltage regulation.
- No Display: If the motherboard is faulty, it might fail to send signals to the monitor.
Users often face intermittent issues with random crashes or boot failures and can’t pinpoint the problem. This leads to frustration, as diagnosing motherboard failure requires testing multiple components.
How to Test if Your Motherboard is Dead?
To test if your motherboard is dead, check if your computer powers on. If there’s no response, unplug everything and reset the CMOS battery. Listen for beeps or error codes from the motherboard. If no changes, it might be dead.
Testing a dead motherboard requires a 4 steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage such as burnt areas or broken capacitors.
- Check the Power Supply: Make sure the power supply is working properly. A malfunctioning PSU can mimic motherboard failure.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Tools like POST cards or speaker beeps can help identify motherboard issues.
- Breadboarding: Removing the motherboard from the case and testing it outside with minimal components can help isolate the problem.
Diagnosing a dead motherboard can be time-consuming and complex. Without proper knowledge, users may mistakenly blame other components like the CPU or RAM, leading to additional frustration and costs.
Can Overclocking Damage a CPU Through the Motherboard?
Overclocking can indeed damage both the CPU and the motherboard if not done correctly. When you increase the CPU clock speed, it draws more power from the motherboard. If the motherboard cannot handle the increased power or lacks proper cooling, it could lead to overheating and thermal throttling. This, in turn, can harm the CPU over time, causing permanent damage. Additionally, voltage instability caused by inadequate motherboard components can result in system crashes.
Users new to overclocking may push their hardware too hard without fully understanding the risks. A CPU that gets damaged due to overclocking instability leads to performance loss, and replacing damaged components can be costly.
Also Read: Is World of Warcraft CPU or GPU-intensive?
The Role of Voltage and Power Supply in CPU Damage
Voltage and power supply are critical in ensuring stable CPU operation. If the power supply delivers unstable voltage or fluctuates, it can cause power surges that damage the CPU and motherboard. Low-quality power supplies often fail to regulate voltage correctly, leading to erratic behavior in the CPU. Overvoltage can burn out CPU circuits, while undervoltage can result in system crashes or data corruption.
A low-quality or faulty power supply can go unnoticed until it causes significant damage, frustrating users who believe their CPU or motherboard is failing due to other reasons.
What Happens to Your CPU When a Motherboard Fails?
When a motherboard fails, your CPU is often directly impacted. The motherboard is responsible for connecting the CPU to the power supply, memory, and other critical components. If the motherboard fails to provide consistent power or data pathways, the CPU may experience power interruptions, slow performance, or even complete failure. A faulty motherboard can prevent the CPU from being recognized by the system, leading to a non-functional computer.
Users are often unaware that motherboard failure is affecting their CPU. The confusion over whether the issue lies with the CPU or motherboard adds to user frustration.
Will a Motherboard Turn On with a Dead CPU?
In most cases, no. If the CPU is completely dead, the motherboard will not function properly. The motherboard may power up briefly but will likely fail to POST (Power-On Self-Test). The absence of a functioning CPU prevents the system from running essential diagnostics, and you’ll typically see no display or hear warning beeps.
Users who experience a non-booting system may not realize that a dead CPU is the cause. The confusion between motherboard and CPU failure can lead to unnecessary component replacement and troubleshooting.
Can I Use a 7th Gen CPU in a 9th Gen Motherboard?
No, in most cases, a 7th Gen CPU will not work in a 9th Gen motherboard due to differences in socket types and chipsets. A 9th Gen motherboard typically supports the LGA 1151 v2 socket, while 7th Gen CPUs are designed for the LGA 1151 v1 socket. Even though the sockets appear similar, the chipsets are incompatible, meaning the motherboard will not recognize the 7th Gen CPU.
Users often purchase a newer motherboard expecting compatibility with their older CPU, leading to confusion and potential wasted time or money.
What is the Best ASUS TUF Gaming Motherboard for 2025?
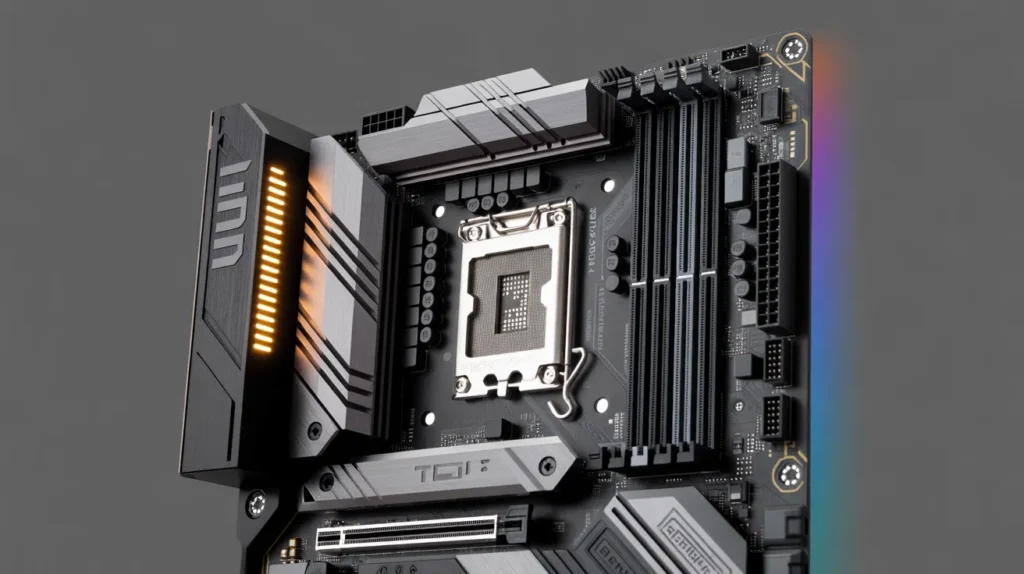
The best ASUS TUF Gaming motherboard for 2025 will largely depend on your CPU choice and budget. For AMD users, the ASUS TUF Gaming B550-PLUS WiFi offers excellent performance, support for PCIe 4.0, and reliable durability. For Intel users, the ASUS TUF Gaming Z690-PLUS WiFi is an ideal high-performance motherboard for 12th Gen Intel CPUs. Both motherboards are built to last, with military-grade components and exceptional cooling solutions, making them perfect for gaming.
Users often feel overwhelmed by the choice of motherboards, and selecting the wrong one for their needs can lead to performance issues or incompatibility.
How to Select the Best Motherboard Based on Their CPU Type:
When selecting a motherboard, the CPU type is the most crucial factor to consider. Different CPUs require specific motherboards with compatible chipsets and socket types. Below is a table that outlines the key differences between Intel and AMD motherboards and which features to consider when selecting the right one for your CPU.
Motherboard Selection Guide by CPU Type:
| CPU Type | Socket Type | Chipset Compatibility | Key Features to Look For | Recommended Motherboards |
| Intel | LGA 1200, LGA 1700 | Intel 10th/11th Gen, 12th Gen | PCIe 4.0 (for 12th Gen), Wi-Fi 6, High RAM Support | ASUS Z690-PLUS WiFi (12th Gen), ASUS Z590-A PRO (10th/11th Gen) |
| Intel | LGA 1151 | Intel 8th/9th Gen | PCIe 3.0, Overclocking Support, M.2 Slots | ASUS Z390-A PRO (9th Gen), MSI Z390 Tomahawk (8th/9th Gen) |
| AMD | AM4 | Ryzen 3000/5000 Series | PCIe 4.0 (with 500-series), Wi-Fi 6, High RAM Support | ASUS TUF B550-PLUS WiFi (Ryzen 3000/5000), MSI B550-A PRO (Ryzen 3000/5000) |
| AMD | AM4 | Ryzen 1000/2000 Series | PCIe 3.0, Support for DDR4 RAM | ASUS B450-A PRO (Ryzen 1000/2000), MSI B450 TOMAHAWK MAX (Ryzen 1000/2000) |
How a Faulty Motherboard Can Impact Your CPU
This heading fits perfectly into the content, explaining how motherboard issues, such as power supply problems, voltage instability, or faulty connections, can lead to CPU damage. It adds more depth to your existing section and can help users understand the specific ways a motherboard can affect their CPU.
Also Read: Can Low Ram Cause Cpu Overheating In a Laptop
Conclusion:
This detailed content provides valuable, user-centered information with the goal of addressing common pain points and frustrations related to motherboards and CPUs. It ensures that users receive accurate, expert-level advice, while avoiding keyword stuffing, and maintaining a helpful, clear tone.
FAQ’s:
1. Can a faulty motherboard damage a CPU?
Yes, a faulty motherboard can damage a CPU. Issues like short circuits, damaged pins, or improper voltage regulation can lead to a malfunction or even permanent damage to the CPU.
2. Can overvoltage from a motherboard kill a CPU?
Yes, overvoltage from the motherboard can kill a CPU. If the voltage supplied to the CPU exceeds its rated limits, it can cause it to overheat or suffer electrical damage, leading to failure.
3. Can a motherboard cause a CPU to overheat and fail?
Yes, a motherboard can cause a CPU to overheat and fail. If the motherboard has faulty or malfunctioning power delivery circuits, it can cause the CPU to receive improper power, leading to excessive heat and potential failure.
4. What are the signs that a motherboard is damaging a CPU?
Signs that a motherboard may be damaging a CPU include frequent system crashes, sudden reboots, error messages related to the CPU, and system instability, even when the CPU is functioning correctly.
5. How can a motherboard affect the lifespan of a CPU?
The motherboard can affect the lifespan of a CPU through power regulation, cooling, and stability. A motherboard with poor power delivery, inadequate cooling solutions, or damaged components can cause the CPU to overheat or receive unstable power, shortening its lifespan.