A CPU’s power use depends on its type and work. Regular CPUs use around 35W to 125W, while powerful ones can go up to 200W or more when under heavy work. The power needed changes based on what tasks the CPU is doing.
This guide will break down the factors influencing CPU power consumption and offer tips for managing it effectively.
How to Accurately Compute CPU Power Consumption: A Step-by-Step Guide:
To compute CPU power consumption accurately, follow these steps: First, identify the CPU’s voltage and current. Then, use the formula: Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A). For precise results, check the CPU datasheet or use software tools that measure real-time power usage.
Follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Gather Information:
Voltage: Check the CPU’s operating voltage, which is often available in the CPU datasheet or through system monitoring tools like BIOS.
Current: Measure the current draw. This value is also found in the datasheet or can be estimated using specialized software or hardware tools.
Step 2: Apply the Power Formula:
To compute power consumption, use the formula:
Power (W)
=
Voltage (V)
×
Current (A)
Power (W)=Voltage (V)×Current (A)
For example, if the CPU operates at 1.2V and draws 50A, the power consumption is:
Power
=
1.2
V
×
50
A
=
60
W
Power=1.2V×50A=60W
Step 3: Use Software Tools for Real-Time Monitoring:
Software tools like HWMonitor, Intel Power Gadget, or AMD Ryzen Master give real-time estimates of CPU power usage under various loads, such as when idle or during heavy tasks like gaming. These tools are also great when comparing the power consumption of Intel vs AMD CPUs to understand which brand is more energy-efficient.
Step 4: Consider Other Important Factors:
Clock Speed: CPUs with higher clock speeds tend to consume more power. This is a critical factor when choosing low-power CPUs for gaming, as you want the best performance with minimal power consumption.
Thermal Design Power (TDP): TDP indicates the maximum amount of heat a CPU generates, which is often a close estimate of its power consumption under load. Power-saving CPUs for laptops typically have a lower TDP, making them ideal for longer battery life.
Step 5: Measure Power Usage Under Different Loads:
For a more accurate reading, use stress testing software like Prime95 or AIDA64 to measure power consumption under various load conditions. This will help you understand how to reduce CPU power consumption during high-performance tasks.
By using the voltage and current values from the datasheet and applying the formula, you can easily compute your CPU’s power usage. For more detailed insights, use real-time monitoring software to track CPU power consumption under different operating conditions. Additionally, if you are looking for low-power CPUs for gaming or power-saving CPUs for laptops, check the TDP values and compare Intel vs AMD for the most energy-efficient options.
How Much Wattage Does a Gaming PC Power Supply Need?
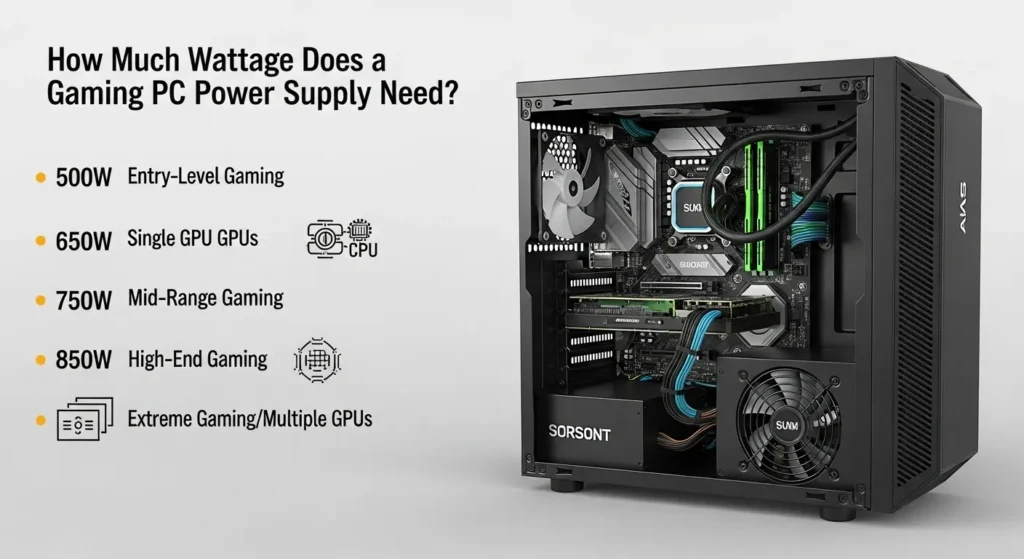
The wattage required for a gaming PC power supply depends on your components. A basic gaming PC needs around 450-550W, while high-end setups with powerful GPUs and multiple drives may require 750W or more.
Here’s a breakdown of wattage requirements based on different setups:
| PC Setup Type | Recommended PSU Wattage | Explanation |
| Basic Gaming PC | 450W – 550W | Ideal for low-power CPUs for gaming, mid-range GPUs, and fewer drives. Works well for most casual gamers. |
| Mid-Range Gaming PC | 550W – 650W | Suitable for gaming PCs with better power-hungry GPUs and a few more components, ensuring smooth gameplay. |
| High-End Gaming PC | 650W – 750W | For high-end CPUs and GPUs (like Intel or AMD’s latest models), multiple storage devices, and overclocking. |
| Enthusiast/Overclocked PC | 750W or higher | For setups with overclocked processors (Intel or AMD), extra powerful GPUs, and advanced cooling systems. |
Key Takeaways:
- Wattage Range: A basic gaming PC with low-power CPUs will need less wattage, but high-performance CPUs and GPUs demand more power.
- Power Efficiency: If you’re concerned about power consumption, opting for low-power CPUs for gaming or power-saving CPUs for laptops can help lower wattage demands while still offering good performance.
- Extra Headroom: Always choose a PSU with some extra wattage to ensure your system runs efficiently and is future-proof. For example, consider power-saving features when comparing Intel vs AMD CPUs.
This simple guide ensures that you pick the right power supply based on your PC’s needs, keeping power consumption in check without sacrificing performance.
Also Read: Is CPU and processor the same?
Power Consumption of Older HEDT and Legacy CPUs: A Detailed Analysis:
Older HEDT CPUs and legacy processors use more power due to outdated technology and larger core counts. Designed for performance, not efficiency, they consume more electricity than modern CPUs. Upgrading to a newer model improves power efficiency, lowers energy consumption, and offers long-term savings with better performance and lower bills.
- Older HEDT and Legacy CPUs: These processors were designed for high performance rather than energy efficiency, leading to higher power consumption compared to modern systems.
- Higher Power Consumption: Due to older technology and larger core counts, these CPUs use more electricity. Unlike newer processors, they don’t have the advanced power management features that reduce energy usage.
- Efficiency Difference: Modern CPUs are built with better power efficiency in mind, offering improved performance while using less power. They are designed to consume less energy, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
- Upgrade Benefits: Upgrading to a newer CPU can significantly reduce power consumption, leading to lower electricity bills and a more efficient system overall. The transition to modern processors can help users save on energy costs and benefit from greener computing.
How much power did a computer consume for an hour?
A computer’s power consumption for an hour depends on its type and usage. For example, a desktop computer typically uses 200-400 watts, while a laptop uses about 50-100 watts. Tasks like gaming or video editing increase power consumption. To get an accurate figure, check the power rating on your device. This helps you understand how much energy your computer consumes over time.
Top Energy-Efficient CPUs for Low Power Consumption in 2025:
In 2025, energy-efficient CPUs are perfect for low power consumption. Processors like the AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D and Intel Core i7-13700K use less energy, making them great for both performance and long battery life. These CPUs are designed to deliver strong performance while saving energy, making them ideal for eco-friendly computing.
| CPU Model | Power Consumption | Key Features |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | Low Power | Advanced 3D V-Cache for better performance and energy efficiency. |
| Intel Core i7-13700K | Energy-Efficient | Great balance of power and performance with low energy usage. |
| Apple M2 | Very Low Power | Highly efficient for laptops and lightweight devices. |
| Intel Core i5-12600K | Moderate Power | Optimized for gaming and productivity with energy savings. |
These processors are ideal for users who want both energy savings and great performance. Whether for gaming, work, or eco-friendly computing, these CPUs deliver!
Comparing Power Consumption: Intel vs AMD CPUs:
When comparing power consumption between Intel and AMD CPUs, AMD processors are generally more power-efficient.
Intel CPUs: Power Consumption Overview:
Intel CPUs generally consume more power due to their focus on high-performance capabilities and faster clock speeds. They are designed for tasks that require strong processing power. Here are key points about Intel’s power consumption:
- Higher Performance = More Power Consumption: Intel processors are built for high performance, which naturally increases energy use.
- Turbo Boost Technology: Intel CPUs often use Turbo Boost, which increases clock speeds during demanding tasks, resulting in higher power draw.
- Efficiency in Newer Models: Modern Intel CPUs, like those based on the 10nm architecture, are more energy-efficient compared to older generations.
Example: The Intel Core i9-12900K has a Thermal Design Power (TDP) of 125W, which means it consumes more power under load compared to many AMD counterparts.
Also Read: Which CPU Clock Speed is Fastest?
AMD CPUs: Power Consumption Overview:
AMD CPUs are known for their energy efficiency, particularly in the Ryzen and Ryzen 7000 series. These processors deliver strong performance while consuming less power than many Intel high-performance chips. Here are some important aspects of AMD’s power consumption:
- Energy Efficiency: AMD’s use of 7nm and 5nm architecture helps reduce power consumption while still maintaining strong processing power.
- Balanced Performance: AMD offers a good balance between performance and energy efficiency, especially in multi-core workloads.
- Lower TDP: AMD processors often have lower TDP (Thermal Design Power) than Intel’s, meaning they consume less power overall.
Example: The AMD Ryzen 7 5800X, with a TDP of 105W, is more power-efficient than many high-end Intel CPUs, offering a good balance between performance and power savings.
Components That Determine PC Power Consumption:
PC power consumption mainly depends on components like the CPU, GPU, power supply unit (PSU), RAM, and storage devices. The CPU and GPU use the most power, especially during demanding tasks like gaming or video editing. Efficient PC power management depends on choosing energy-efficient parts and reducing unnecessary usage, helping save electricity. Additionally, optimizing the power supply unit and hardware settings can reduce overall consumption.
FAQ’s:
1. Does CPU power consumption vary depending on the workload?
Yes, the power consumption of a CPU increases with higher workloads such as gaming, video editing, or running intensive applications.
2. Can overclocking a CPU increase its power consumption?
Yes, overclocking a CPU can lead to a higher power draw because it operates at higher clock speeds and voltages.
3. Does a higher-end CPU consume more power than a budget CPU?
Yes, typically, high-performance CPUs with more cores and higher clock speeds consume more power compared to budget or low-power CPUs.
4. How can I calculate the power consumption of my CPU?
To calculate the power consumption of your CPU, you can look at its TDP (Thermal Design Power), which is usually provided by the manufacturer, and consider the overall system power usage with a power meter.
5. What factors influence the power consumption of a CPU?
CPU power consumption is influenced by factors like clock speed, number of cores, voltage, workload, and the efficiency of the CPU architecture.
Conclusion:
Understanding CPU power consumption is essential for optimizing performance and energy efficiency. By considering factors like voltage, current, clock speed, and workload, users can calculate and manage their CPU’s power usage effectively. Choosing energy-efficient CPUs, like those from AMD and Intel, can also help reduce electricity consumption, leading to better performance with lower environmental impact.
Also Read: What is the best i7 CPU